The globalization transformed the way we do business. Companies have diverse customers from all around the world with different backgrounds and the internet has created an equal playing field for international competition. Because of that, CULTURE has become one of the momentous business topics of 2020. More and more HR Leaders now recognize that culture is one of the distinctly important elements, which drive people’s behavior, innovation and customer service. All of those points are essential for the development of company.
What is Culture?
Before we talk about cross cultural competence, let us have a comprehensive understanding of the abstract concept of “CULTRUE”!
‘Every man is in certain respects a. like all other men, b. like some other men, c. like no other man.’ (Kluckhohn et al., 1953, p. 53) Point b. of this popular quote refers to the affiliation of people to specific cultures. However, this in no way defines the composition of these cultures or how they differentiate from one another, who belongs to them and what cultural differences can materialize in certain situations. Culture is used as a multi-purpose term depending on the perception, definition and usage, different aspects are emphasized. Here, one particular interpretation of culture among many is presented that has proven itself in international collaboration:
Culture as a system of orientation is the characteristic element of this definition: Culture is a system of ‘rules of the game’ around which members of a specific culture orient themselves in order to organize living together within a community as smoothly as possible.
Customers’ Culture Cross Culture Competence
The consumers’ behaviours are strongly influenced by their culture. Culture or you can say their cultural backgrounds strongly impact the way customers respond to products, services and marketing campaigns. Because of that, companies are required to operate on a multi cultural paradigm with various perspectives. Thanks to the development of Internet, most businesses naturally have a global reach, so companies must understand how powerful culture can influence their target customers. With fully understanding of their customers’ culture will help companies choose better ways to deliver and market culturally sensitive products and services.
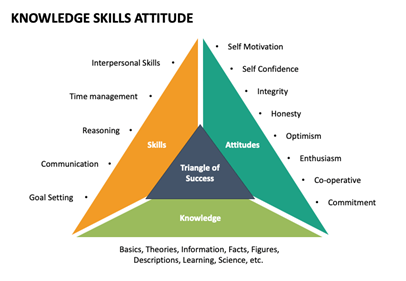
Cross Culture Competence
When people from different cultures meet, initially, the obvious differences are of course apparent, such as appearance, language, clothing, food, architecture and rules of etiquette. This is known as evident culture, because cultural features are immediately evident.
As such, the following definition of cross-cultural competence is a useful basis for further debate and elaboration: the abilities that enable one to operate effectively in different cultures.
The following three patterns may help have a better understanding of cross culture competence: A) “KNOWLEDGE” begins with an awareness of one’s own culture and includes an understanding of culture and cultural differences using schemata or frameworks, progressing towards an increasingly complex understanding of the sources, manifestations, and consequences of a particular culture. B) “AFFECT’” includes attitudes toward other cultures and the motivation to learn about and engage with them. Openness and empathy are of particular importance in this component. C) “SKILLS”, which encompass the ability to regulate one’s own reactions in a cross-cultural setting, interpersonal skills, and the flexibility to assume the perspective of someone from other cultures.
Employees with Cross Culture Competence
Employees with strong cross culture competence are knowledgeable of and interact effectively with customers and business partners of different racial, ethnic and social background. Domestically, the working market and workforce are also gradually shifting to becoming more culturally diverse. Being capable of cross culture communication is seen positive for companies who operate on a global scale. It has already been proven by diverse market economy researches that companies who prioritize creating a company culture of diversity and hiring employees with strong cross culture competence could make longstanding benefits. Those employees offer different cultural perspectives that are extremely useful in achieving a variety of business objectives in areas like new products and marketing.
Where can Companies start?
- Culture cannot be delegated—it must be on the top of CEO’s list:
CEOs and HR leaders must clearly understand their company’s cultural values, determine how they relate to business strategy, and take responsibility for shaping them, while also analyzing whether their own behaviors reinforce the desired culture.
- Understand both own and target culture:
Business leaders should closely examine their business processes step by step to identify which requirements and practices and are aligned with the target culture and adjust its strategies in time to set up sustained competitive advantages. While many HR organizations are just focusing on building teams to better communicate leaders’ vision of the desired culture, mean time they also need to realize that, self-awareness about own cultural identity is as much important as the awareness about the cultures of clients.
- Determine whether the targeted culture is taking hold:
Executives can drive permanent cultural change throughout the organization by reminding employees that culture is a tangible set of attributes and behaviors. Through suitable culture coaching program help employees clearly recognized at visible “touchpoints” among them and clients and partnerships.
- Measure culture:
Without measurements about Cross Culture Competence, all efforts on competence coaching will be like carry coals to Newcastle. Companies can use empirical tools to analyze and measure employee attitudes and actions. If measurement reveals that current behaviors have conflicts with target culture. HR should take the lead in the effort to refine the program to communicate and model culture throughout the organization.